No products in the cart.
Return To Shop 0 Cart $0.00 0
No products in the cart.
Return To Shop Shopping cart (0)
Subtotal: $0.00
Free shipping over 299$
Cellulitis Infection: Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Cellulitis infection is a serious bacterial skin condition that can quickly spread and lead to severe health complications if not treated promptly. Often beginning as a simple red patch on the skin, cellulitis can rapidly progress, affecting deeper layers and potentially spreading to the bloodstream. Recognizing the warning signs of cellulitis infection can help you seek medical care in time to avoid serious outcomes. The common symptoms of cellulitis, its causes, and when to seek emergency care.
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that usually occurs when bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, enter the skin through a break or crack. This can happen due to cuts, scrapes, insect bites, or other skin conditions that weaken the skin barrier. The infection generally affects the lower legs, though it can appear anywhere on the body.
Related Articles: Why Cellulitis Infection is So Dangerous
Common Warning Signs of Cellulitis Infection
Understanding the early warning signs of cellulitis can help prevent the infection from spreading and becoming life-threatening. Here are the most common symptoms to watch out for:
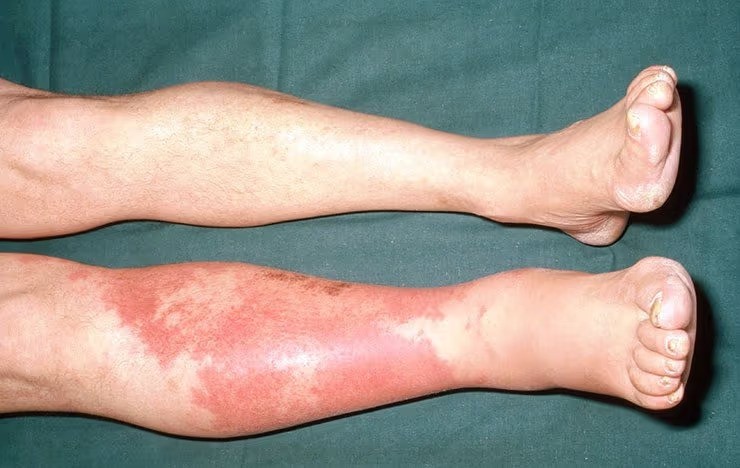
1. Redness and Swelling
One of the earliest signs of cellulitis infection is a red, swollen area on the skin. The area might feel warm to the touch and may spread if the infection worsens. The redness may not appear clearly defined, but it typically covers a large portion of the affected area.
2. Pain and Tenderness
Infected areas are often painful to touch and may feel tender or sore, even without direct pressure. Pain can range from mild discomfort to severe throbbing as the infection progresses. This tenderness often intensifies over time and can become extremely uncomfortable.
3. Skin That Feels Warm
A characteristic symptom of cellulitis infection is skin that feels noticeably warmer than the surrounding areas. This warmth occurs due to increased blood flow in response to infection, which may intensify as the infection spreads.
4. Blisters or Pus
In more advanced cases, cellulitis can cause blisters or pus-filled bumps on the skin. These may ooze or leak fluid if they burst. Blisters indicate that the infection has penetrated deeper into the skin layers, requiring immediate medical intervention.
5. Fever and Chills
When cellulitis infection starts to spread, it may trigger a fever and chills. This is a sign that the infection has begun affecting the body systemically. Even a low-grade fever indicates that the infection may be progressing and needs prompt medical attention.
6. Red Streaks on the Skin
Red streaks radiating from the infected area often signal that the infection is spreading into the lymphatic system. These streaks can be a sign of lymphangitis, a potentially serious condition. If you notice red streaks, it’s essential to seek immediate medical care, as this indicates a high risk of further spread.
7. Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes near the infected area may become swollen or tender to the touch. Swollen lymph nodes are an indication that your body is trying to fight off the infection, and their enlargement is often a response to bacterial spread. This symptom is more likely in advanced cases and can accompany other symptoms like fever or chills.
8. Fatigue and Muscle Aches
A severe cellulitis infection can cause symptoms that affect your entire body, including fatigue and muscle aches. This general feeling of malaise indicates that your immune system is working hard to fight the infection. If cellulitis reaches this stage, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cellulitis Infection
Several factors can increase the risk of cellulitis infection:
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or insect bites can allow bacteria to enter the skin.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, have a higher risk of infection.
- Chronic Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema or athlete’s foot can create open sores or breaks in the skin that increase susceptibility to cellulitis.
- Obesity: Obesity can lead to poor blood circulation, making it easier for infections to develop.
- Lymphedema: Swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly in the arms and legs, can make it easier for bacteria to enter.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Cellulitis infection is considered a medical emergency if it spreads rapidly or causes severe symptoms. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Increasing pain, redness, or swelling in the affected area
- Fever or chills that accompany skin symptoms
- Red streaks radiating from the infection site
- Tender or swollen lymph nodes
If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to complications such as abscesses, septicemia (blood poisoning), or gangrene, all of which require immediate care.
Treatment Options for Cellulitis Infection
Once cellulitis infection is diagnosed, doctors typically prescribe antibiotics to help combat the bacteria. These may be taken orally or administered intravenously for severe cases. Over-the-counter pain relievers and warm compresses can help reduce pain and swelling. Following your doctor’s instructions and completing the full course of antibiotics is critical to fully eliminate the infection and prevent recurrence.
Related Articles: Effective Cellulitis Treatments: Your Complete Guide to Healing
Preventing Cellulitis Infection
Preventing cellulitis infection involves maintaining good hygiene and taking care of any skin injuries immediately. Here are some effective prevention tips:
- Clean and Cover Wounds: Clean cuts or scrapes promptly with soap and water, and apply an antibiotic ointment.
- Keep Skin Moisturized: Dry skin is more prone to cracks, which can be entry points for bacteria.
- Avoid Scratching: Avoid scratching itchy areas, particularly if you have eczema, as it can create open wounds.
- Manage Pre-existing Skin Conditions: If you have chronic skin conditions, work with a dermatologist to keep them under control.
Final Thoughts
Cellulitis infection is not only painful but also potentially dangerous if it spreads unchecked. By understanding the warning signs and taking preventative measures, you can reduce your risk of developing cellulitis. Always consult a healthcare professional at the earliest signs of infection, as prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure a quick recovery.
More
More

