Bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin condition characterized by itchy, blistering lesions that can be both painful and distressing. While medical treatment is essential, your diet can also play a role in managing the symptoms. Certain foods may trigger inflammation or worsen the condition, making it crucial to know what to avoid. Here’s a comprehensive guide to foods you should consider cutting out to help manage bullous pemphigoid effectively.
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
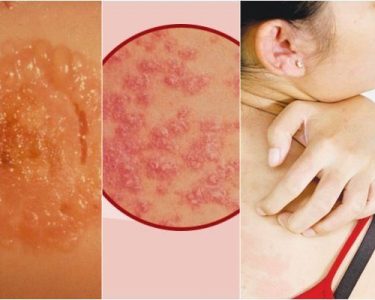
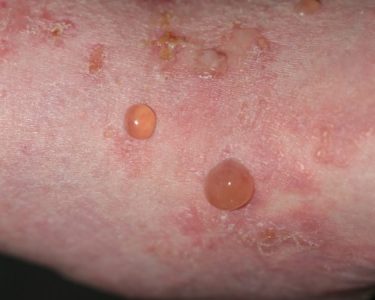
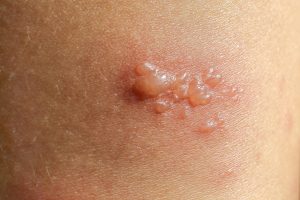
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare but serious autoimmune skin disorder characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters (bullae) that form on the skin. These blisters often develop on areas prone to friction, such as the arms, legs, or abdomen. Although the condition is more common in older adults, it can affect individuals of any age.
Causes and Mechanism
The condition arises when the immune system mistakenly attacks the tissues that connect the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) to the underlying layer (dermis). Specifically, autoantibodies target proteins in the basement membrane, a thin layer that anchors the epidermis. This immune response leads to inflammation and separation of the skin layers, causing blister formation.
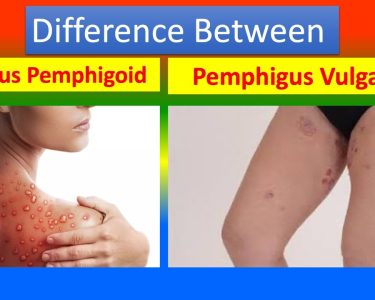
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid vs Pemphigus Vulgaris: Treatment Options You Need to Know
The exact cause of this immune dysfunction is unknown, but triggers may include:
- Medications: Some drugs, such as loop diuretics, penicillin, or NSAIDs, have been linked to bullous pemphigoid.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections may trigger the condition.
- Other medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes or neurological diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, may increase the risk.
Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid
The symptoms can vary in severity but often include:
- Blisters: The hallmark symptom is the development of large, tense blisters filled with clear fluid, which do not easily rupture.
- Itching: A persistent and often severe itch may occur before blisters form.
- Skin redness and inflammation: Areas surrounding the blisters may appear red or swollen.
- Mucosal involvement: In some cases, lesions may form in the mouth or other mucous membranes.
Who is at Risk?
Bullous pemphigoid primarily affects individuals over the age of 60. While the condition is not contagious, certain factors may increase the likelihood of its development:
- Advanced age
- A history of autoimmune disorders
- Long-term medication use
- Neurological conditions
Why Diet Matters in Bullous Pemphigoid
Although no specific diet cures bullous pemphigoid, avoiding inflammatory or allergenic foods can help reduce flare-ups. An anti-inflammatory diet supports your immune system and may help to minimize the severity of symptoms.
Top Foods to Avoid with Bullous Pemphigoid
1. Processed and Fried Foods
- Why Avoid? Processed and fried foods are rich in trans fats, which can increase inflammation.
- Examples to Cut: Chips, fried chicken, processed meats, and packaged snacks.
2. Sugary Foods and Beverages
- Why Avoid? Excessive sugar intake can spike blood sugar levels and trigger inflammatory responses.
- Examples to Cut: Soda, candy, baked goods, and sugary cereals.
3. Gluten-Containing Foods
- Why Avoid? Some individuals with autoimmune conditions are sensitive to gluten, which can exacerbate inflammation.
- Examples to Cut: Bread, pasta, cakes, and other wheat-based products.
4. Dairy Products
- Why Avoid? Dairy can be inflammatory for some people, especially those who are lactose intolerant or have dairy sensitivities.
- Examples to Cut: Milk, cheese, cream, and butter.
5. Nightshade Vegetables
- Why Avoid? Nightshades contain solanine, a compound that may contribute to inflammation in some individuals.
- Examples to Cut: Tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, and potatoes.
6. Alcohol
- Why Avoid? Alcohol can weaken the immune system and irritate the skin, making symptoms worse.
- Examples to Cut: Beer, wine, cocktails, and spirits.
7. Spicy Foods
- Why Avoid? Spices can irritate sensitive skin and potentially worsen itching or blistering.
- Examples to Cut: Hot peppers, chili powder, and certain spicy sauces.
8. High-Histamine Foods
- Why Avoid? Histamine-rich foods may trigger allergic-like reactions in some people.
- Examples to Cut: Aged cheeses, fermented foods, smoked meats, and canned fish.
Tips for Building a Bullous Pemphigoid-Friendly Diet
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune condition characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. Managing BP typically involves medications, but diet can also play a crucial role in supporting the immune system and reducing inflammation. While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for those with BP, certain foods can help reduce flare-ups and promote overall health. In this article, we’ll explore practical tips for building a bullous pemphigoid-friendly diet.
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid – Autoimmune Skin Disorder
1. Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Since BP involves inflammation, choosing foods that can help reduce inflammation in the body is important. Some key anti-inflammatory foods to include are:
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines can help reduce inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with antioxidants that help combat inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds provide healthy fats and anti-inflammatory properties.
2. Focus on High-Fiber, Whole Foods
A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods can help improve digestion and overall health, which may indirectly benefit those with BP. Focus on:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats provide fiber, which supports gut health.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Choose a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure you’re getting a broad range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber and plant-based protein.
3. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
Processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined carbohydrates can increase inflammation in the body. People with BP should consider reducing their intake of:
- Sugary Beverages: Soft drinks, fruit juices, and energy drinks can spike blood sugar levels and contribute to inflammation.
- Processed Meats: Sausages, hot dogs, and other processed meats are often high in unhealthy fats and preservatives.
- Refined Grains: White bread, pastries, and pasta made from refined flour can have similar inflammatory effects.
4. Avoid Food Triggers (If Identified)
Some individuals with BP may have specific food sensitivities or allergies that can exacerbate symptoms. Common food triggers might include:
Related Articles: Bullous Pemphigoid Natural Treatment and Some Food Avoid
- Dairy Products: For some, dairy may contribute to inflammation or worsen skin conditions.
- Nightshades: Tomatoes, potatoes, and peppers are part of the nightshade family, which may trigger inflammatory reactions in some individuals.
- Gluten: Some people with autoimmune diseases, including BP, find that gluten worsens their symptoms. Consider gluten-free options if you suspect gluten sensitivity.
5. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can worsen skin conditions, so it’s essential to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day, or more if you are active or in hot climates. Hydrating not only supports your skin health but also helps flush toxins from your body.
6. Add Probiotic-Rich Foods for Gut Health
The gut plays a significant role in immune function, and a healthy gut microbiome may help manage autoimmune diseases. Including probiotic-rich foods in your diet can be beneficial:
- Yogurt (if tolerated): Look for unsweetened, live-culture yogurt.
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink that provides probiotics.
- Sauerkraut and Kimchi: Fermented vegetables that are naturally rich in probiotics.
7. Ensure Sufficient Protein Intake
Protein is essential for skin repair and immune function. Since BP can cause skin damage, it’s crucial to ensure adequate protein intake. Sources of protein include:
- Lean Meats: Skinless chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Tofu, tempeh, edamame, and legumes.
- Eggs: A great source of high-quality protein and essential amino acids.
8. Include Vitamin-Rich Foods for Skin Health
Certain vitamins and minerals are important for skin health, and deficiencies can worsen BP symptoms. Include foods rich in these essential nutrients:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli. Vitamin C helps with collagen production and skin repair.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant found in nuts, seeds, spinach, and avocados that supports skin healing.
- Zinc: Important for immune function and wound healing, found in pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, and lentils.
9. Consult a Dietitian or Healthcare Provider
Before making any significant changes to your diet, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or dietitian, especially if you are on medication or have other health conditions. A professional can help you create a personalized plan that meets your specific nutritional needs.
Related Articles: 8 Natural Remedies for Bullous Pemphigoid
Conclusion
Managing bullous pemphigoid requires a holistic approach that includes both medical care and dietary awareness. By avoiding inflammatory and allergenic foods, you can help reduce flare-ups and support your body’s healing process. Start cutting out these problematic foods today to take control of your symptoms and improve your quality of life.