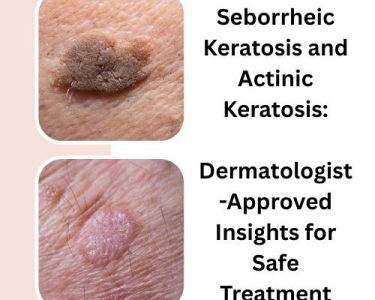
Actinic keratosis (AK) is a common skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, resulting in rough, scaly patches on the skin. Left untreated, actinic keratosis can potentially progress to squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer. This underscores the importance of timely and effective treatment. We explore the most effective treatment options for actinic keratosis, helping you understand the best ways to manage and treat this condition.
Related Article: 11 Natural Treatments for Actinic Keratosis
1. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, also known as cryosurgery, is one of the most widely used treatments for actinic keratosis. This procedure involves applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area, freezing the abnormal cells. The freezing process causes the lesion to blister and eventually peel off, allowing new, healthy skin to form. Cryotherapy is quick, minimally invasive, and effective, making it a preferred choice for treating single or small numbers of actinic keratoses.
2. Topical Medications
Topical medications are another effective treatment option for actinic keratosis, especially when multiple lesions are present. These medications are applied directly to the skin and work by destroying abnormal cells or boosting the body’s immune response to target these cells. Some of the commonly used topical treatments include:
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU): A chemotherapy cream that targets and destroys rapidly growing abnormal skin cells.
- Imiquimod: An immune response modifier that helps the body recognize and attack abnormal cells.
- Diclofenac: A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) gel that reduces inflammation and destroys abnormal cells.
- Ingenol mebutate: A topical gel that quickly induces cell death in abnormal cells and also stimulates an immune response.
Topical treatments may cause side effects such as redness, swelling, and peeling, but these are typically temporary and resolve after treatment completion.
Related Article: Actinic Keratosis on the Eyelids: Protect Your Eyelids
3. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Photodynamic therapy is a highly effective treatment for actinic keratosis, particularly for patients with multiple or widespread lesions. PDT involves the application of a photosensitizing agent, usually in the form of a cream, to the affected skin. After allowing time for the cream to be absorbed, the area is exposed to a specific wavelength of light, which activates the photosensitizer. This activation destroys the abnormal cells while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue.
PDT is effective and has the added benefit of minimal scarring. However, it may cause temporary pain, redness, and swelling in the treated area. Patients undergoing PDT are also advised to avoid direct sunlight for a period following treatment, as the skin will be highly sensitive to light.
4. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, causing the outer layers to exfoliate and peel off. This process removes the damaged cells and encourages the growth of new, healthy skin. Chemical peels can effectively treat actinic keratosis by targeting superficial lesions and improving the overall appearance of sun-damaged skin. Commonly used agents for chemical peels include trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and glycolic acid.
While chemical peels can be effective, they may cause side effects such as redness, peeling, and sensitivity, particularly in patients with sensitive skin.
5. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses focused light energy to remove abnormal cells in the upper layers of the skin. This treatment option is effective for actinic keratosis and can also improve the texture and appearance of sun-damaged skin. Lasers such as the CO2 and erbium are commonly used for this purpose.
Laser therapy is precise and can target specific areas without affecting surrounding tissue. However, it may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired results and can be associated with side effects like redness, swelling, and a risk of infection.
Related Article: What Causes Actinic Keratoses Medical Treatment and Home Remedies
6. Curettage and Electrosurgery
This procedure involves scraping off the lesion with a curette, a sharp, spoon-like instrument, followed by the use of an electric needle to destroy any remaining abnormal cells. Curettage and electrosurgery are effective for thicker or more resistant actinic keratoses. This method can be slightly more invasive than others, but it is highly effective for treating isolated lesions.
7. Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a mechanical exfoliation technique that removes the outer layers of the skin using a rotating abrasive tool. This procedure can effectively remove actinic keratosis lesions and improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin. Dermabrasion may require local anesthesia and can result in redness and swelling during the healing process.
Conclusion
Actinic keratosis is a condition that requires timely and effective treatment to prevent potential progression to skin cancer. The most effective treatment for actinic keratosis varies depending on the number, size, and location of lesions, as well as individual patient factors. Options such as cryotherapy, topical medications, photodynamic therapy, chemical peels, laser therapy, curettage and electrosurgery, and dermabrasion provide a range of effective methods to manage and treat this condition. Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Related Article: Actinic Keratosis – Actinic Cheilitis
By understanding and utilizing these treatments, individuals can effectively manage actinic keratosis and maintain healthier skin.