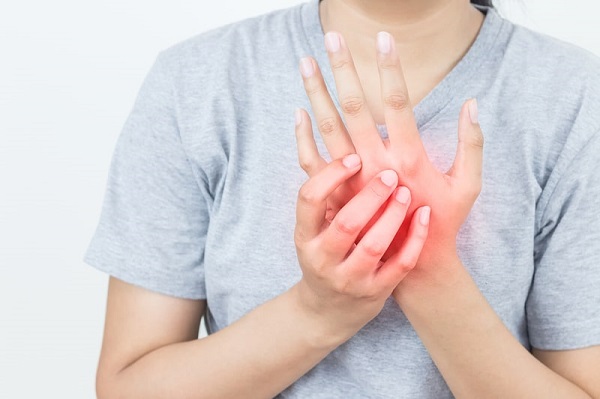
Peripheral neuropathy in hands and fingers is a condition that results from damage to the peripheral nerves, causing discomfort, weakness, or loss of sensation in these areas. This condition can significantly impact daily life and, if left untreated, may lead to irreversible nerve damage. Recognizing the early signs is crucial for seeking timely intervention. Here’s what you need to know about the symptoms, causes, and potential treatments for peripheral neuropathy in hands and fingers.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that results from damage to the peripheral nerves—the intricate network of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves play a critical role in transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, including the arms, legs, and internal organs. When they are damaged, it can disrupt this communication, leading to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Related Articles: Say Goodbye to Peripheral Neuropathy Pain: Effective Treatments You Need to Know
Types of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can be classified based on the type of nerves affected:
- Sensory Neuropathy: Affects the sensory nerves, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Motor Neuropathy: Impacts motor nerves, causing muscle weakness and coordination problems.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Involves autonomic nerves, which control involuntary functions like blood pressure, digestion, and heart rate.
- Mixed Neuropathy: A combination of two or more types, leading to a range of symptoms.
Related Articles: Effective Ways to Recovery of Peripheral Neuropathy with Home Remedies
Common Signs of Peripheral Neuropathy in Hands and Fingers
- Tingling or Numbness
- One of the earliest and most common symptoms, tingling or numbness often starts in the fingers and can gradually spread to the hands. Many describe it as a “pins-and-needles” sensation.
- Burning Sensation
- A persistent burning feeling in the fingers or hands might indicate nerve damage. This symptom often worsens at night.
- Sharp or Electric-Like Pain
- Intermittent shooting pains or electric shock-like sensations are telltale signs of nerve irritation.
- Weakness in Hands
- Difficulty gripping objects, opening jars, or performing fine motor tasks can occur as the muscles weaken.
- Increased Sensitivity
- Some individuals experience heightened sensitivity to touch, where even light pressure or contact can cause discomfort.
- Lack of Coordination
- Peripheral neuropathy can affect coordination, making tasks that require precision, such as typing or buttoning a shirt, more challenging.
Related Articles: 10 Natural Remedies for Peripheral Neuropathy
Potential Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy in Hands and Fingers
Understanding the underlying causes of peripheral neuropathy is vital for effective treatment. Common causes include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical injuries, including fractures or repetitive strain, can harm peripheral nerves.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins, especially B vitamins, can impair nerve health.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can contribute to nerve inflammation and damage.
- Toxins and Alcohol: Prolonged exposure to toxins or excessive alcohol consumption can damage nerves.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections like shingles can trigger nerve pain and damage.
Related Articles: Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy by Natural Herbal Remedies
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in your hands and fingers, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis can help prevent complications and identify the root cause. Ignoring symptoms could lead to permanent nerve damage or reduced quality of life.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy in Hands and Fingers
Peripheral neuropathy, a condition affecting the peripheral nerves, can cause discomfort, pain, and loss of function in various parts of the body, including the hands and fingers. Understanding the Treatment for Peripheral neuropathy options available is essential for managing symptoms effectively and improving quality of life.
Related Articles: Peripheral Neuropathy and Diabetes: Top Foods to Protect Your Nerves
Medical Treatments
- Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen or ibuprofen may help alleviate mild symptoms.
- Prescription Medications: Doctors often prescribe anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin or pregabalin) or antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) for nerve pain relief.
- Topical Treatments: Creams containing capsaicin or lidocaine patches can be directly applied to the hands and fingers to reduce pain.
- Physical Therapy Engaging in targeted physical therapy exercises can help strengthen muscles, improve coordination, and reduce pain. Therapists may recommend specific hand and finger exercises to restore dexterity and function.
- Surgery In cases where neuropathy is caused by physical compression of nerves, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure and restore nerve function.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) This non-invasive therapy involves using a device that sends low-voltage electrical currents to the nerves, helping to alleviate pain and improve circulation in the affected areas.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Nutritional Support
- Vitamin Supplements: Deficiencies in vitamins like B12 and E can exacerbate neuropathy symptoms. Supplementing these vitamins may improve nerve health.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients for nerve repair.
- Exercise Regular low-impact activities like yoga, swimming, or walking can enhance blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote nerve health.
- Stress Management Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels, which may otherwise aggravate neuropathy symptoms.
- Avoiding Toxins Limiting exposure to alcohol, tobacco, and other harmful substances can prevent further nerve damage and improve overall health.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate nerves and relieve pain.
- Herbal Remedies Some individuals find relief using herbal supplements for peripheral neuropathy like alpha-lipoic acid or evening primrose oil, though consulting a healthcare provider before starting any supplement is advised.
- Massage Therapy Regular massages can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate discomfort in the hands and fingers.
Preventive Measures
Preventing peripheral neuropathy in hands and fingers involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and protecting nerve health. Key preventive strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Staying active improves blood flow and nerve function.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a nutrient-rich diet supports overall health and prevents deficiencies.
- Protecting Hands: Use gloves or ergonomic tools to reduce strain and prevent injuries.
- Routine Health Checks: Regular check-ups can help detect conditions like diabetes early, reducing the risk of neuropathy.
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy in hands and fingers can significantly affect your quality of life, but recognizing the signs early can lead to effective management and treatment. Don’t ignore symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or pain. Consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and start on the path to recovery. Taking proactive steps to protect your nerve health is essential for long-term well-being.