Tinea versicolor, a common fungal skin infection, can cause discoloration and patches on the skin that appear lighter or darker than the surrounding areas. While it’s often treatable, some individuals experience persistent or recurrent cases, leading to what is commonly referred to as “permanent tinea versicolor.” In such cases, understanding the best medical treatments and remedies becomes essential for effective management and recovery. This article explores the medicines, supplements, and lifestyle changes that can help treat permanent tinea versicolor, with a focus on the role of supplements for tinea versicolor as a complementary approach.
What is Tinea Versicolor?
Tinea versicolor, also known as pityriasis versicolor, is a common fungal skin condition that affects the pigmentation of the skin. It is caused by an overgrowth of yeast known as Malassezia, which naturally resides on the skin. Under certain conditions, this yeast grows uncontrollably, leading to the development of the condition.
While it is not harmful or contagious, tinea versicolor can cause noticeable changes in the skin’s appearance, which may impact self-esteem and confidence.
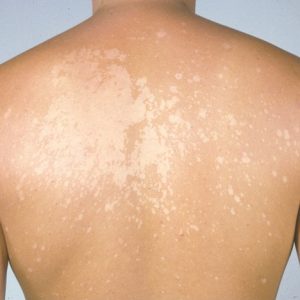
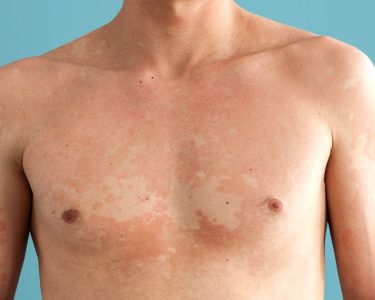
What Does Tinea Versicolor Look Like?
Tinea versicolor typically appears as patches of discolored skin. These patches can be:
- Lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
- Pink, red, tan, or white in color.
- Smooth to the touch but may sometimes feel dry or scaly.
The affected areas are most commonly found on the:
- Chest
- Back
- Neck
- Arms
The patches often become more noticeable when exposed to sunlight because the affected skin doesn’t tan as the surrounding skin does.
Causes of Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor occurs when the balance of yeast on the skin is disrupted. Factors that can contribute to this include:
- Hot and humid climates
- Excessive sweating
- Oily skin
- Weakened immune system
- Hormonal changes
These factors create an environment in which the yeast can thrive and multiply, leading to visible symptoms.
Topical Treatments for Permanent Tinea Versicolor
Topical antifungal medications are often the first line of Herbal treatment for tinea versicolor. These are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin to combat the overgrowth of Malassezia. For persistent cases, the following options are commonly recommended:
1. Azole Antifungal Creams
Medications like clotrimazole, ketoconazole, and miconazole are effective in reducing fungal growth. These creams are applied once or twice daily to the affected areas for several weeks until symptoms improve.
2. Selenium Sulfide
Selenium sulfide, available as a lotion or shampoo, is a powerful antifungal agent that works by reducing yeast levels on the skin. It’s often used as a wash, left on the skin for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off.
3. Ciclopirox
Ciclopirox is another antifungal cream or gel that’s effective for resistant cases. It’s particularly useful when other topical treatments fail.
4. Sulfur-based Ointments
Sulfur-based products are natural antifungal agents that can be used for mild cases of tinea versicolor. They’re less commonly prescribed but are an option for those seeking gentler solutions.
Oral Medications for Persistent Tinea Versicolor
When topical treatments aren’t enough to resolve the infection, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. These are particularly useful for treating widespread or recurrent infections. Common oral medications include:
1. Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an oral antifungal medication that’s often used to treat stubborn cases of tinea versicolor. A typical dosage involves taking one tablet weekly for 2-4 weeks. It’s highly effective but should only be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects.
2. Itraconazole
Itraconazole is another systemic antifungal drug that targets Malassezia. It’s usually taken daily for a week or as a single-dose treatment. Like fluconazole, itraconazole should be used with caution.
3. Ketoconazole (Oral)
Oral ketoconazole is effective but less commonly prescribed due to its potential for liver toxicity. It’s typically reserved for severe or resistant cases of tinea versicolor.
Supplements for Tinea Versicolor
While antifungal medications form the cornerstone of treatment, supplements can play a supportive role in managing and preventing tinea versicolor. Certain nutrients and natural compounds help strengthen the immune system, balance the skin’s microbiome, and reduce the risk of recurrence. Here are some supplements for tinea versicolor worth considering:
1. Probiotics
Probiotics support gut health and improve the body’s immune response, which can help prevent fungal overgrowth. A balanced gut microbiome is critical for reducing systemic inflammation and maintaining healthy skin.
- Recommended Sources: Yogurt, kefir, or probiotic capsules containing strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
2. Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a vital role in skin health and immune regulation. Low levels of vitamin D are linked to an increased risk of fungal infections.
- Dosage: 1000-2000 IU daily, or as recommended by your doctor.
3. Zinc
Zinc has antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a valuable supplement for those with recurring skin infections.
- Sources: Zinc supplements or foods like shellfish, pumpkin seeds, and fortified cereals.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the irritation and redness associated with tinea versicolor.
- Sources: Fish oil supplements, flaxseeds, or walnuts.
5. Selenium
Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that can help control fungal growth. Selenium sulfide shampoos are commonly used topically, but dietary selenium can also be beneficial.
- Sources: Brazil nuts, seafood, and selenium supplements.
6. Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be taken as a supplement or incorporated into your diet.
- Dosage: 500-1000 mg of curcumin daily, or as directed by your healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Treatment
In addition to medications and supplements, certain lifestyle changes can enhance treatment outcomes and prevent recurrence:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Regularly washing the skin with antifungal or medicated cleansers can help keep fungal growth in check. Avoid using oily products that may exacerbate the condition.
2. Wear Breathable Clothing
Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments. Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce sweating and irritation.
3. Avoid Excessive Heat and Humidity
Try to stay in cool, dry environments as much as possible. Use air conditioning or fans to reduce sweating.
4. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration supports overall skin health and helps maintain the skin’s natural barrier against infections.
5. Use Sunscreen
Tinea versicolor patches may become more noticeable after sun exposure. Using sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can help protect the skin and minimize discoloration.
Preventing Recurrence
For individuals dealing with persistent or recurrent tinea versicolor, prevention is key. Here are some strategies to minimize the risk of flare-ups:
- Regular Antifungal Maintenance: Using antifungal shampoos or body washes weekly can help prevent overgrowth of Malassezia.
- Boost Immunity: A strong immune system can reduce susceptibility to fungal infections. Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Avoid Oily Skincare Products: Use non-comedogenic products that won’t clog pores or exacerbate fungal growth.
- Treat Underlying Conditions: Address hormonal imbalances, diabetes, or other factors that may contribute to fungal overgrowth.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist despite using medications, supplements, and lifestyle changes, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist. Chronic or permanent tinea versicolor may require advanced treatment strategies, including long-term antifungal therapies or a combination of oral and topical medications.
Additionally, any signs of severe skin irritation, infection, or scarring should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions and ensure appropriate treatment.
Final Thoughts
Treating permanent tinea versicolor requires a multifaceted approach, combining effective antifungal medications, supportive supplements, and preventive measures. While topical and oral antifungal treatments remain the gold standard, incorporating supplements for tinea versicolor, such as probiotics, vitamin D, and zinc, can boost the immune system and promote long-term skin health. By adopting a comprehensive treatment plan and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, it’s possible to manage this persistent condition and restore healthy, even-toned skin.